
ARE COCKROACHES DANGEROUS? HEALTH RISKS, MYTHS & FACTS ABOUT COCKROACHES
Introduction
If you’ve ever flipped on the kitchen light at night and seen a cockroach dash across the floor, you’re not alone. Cockroaches are one of the most common household pests worldwide—found in homes, restaurants, offices, and even hospitals from New York to New Delhi. But are they just unpleasant roommates, or do they pose a real danger to humans and pets?
Short answer:
Yes, cockroaches can be dangerous—not because of their bite, but due to the germs and allergens they carry. In this article, we’ll break down the science, shatter myths, and give you practical tips to protect your home.
[Image Suggestion 1: High-resolution macro shot of a cockroach in a kitchen setting, showing detail and clarity.]
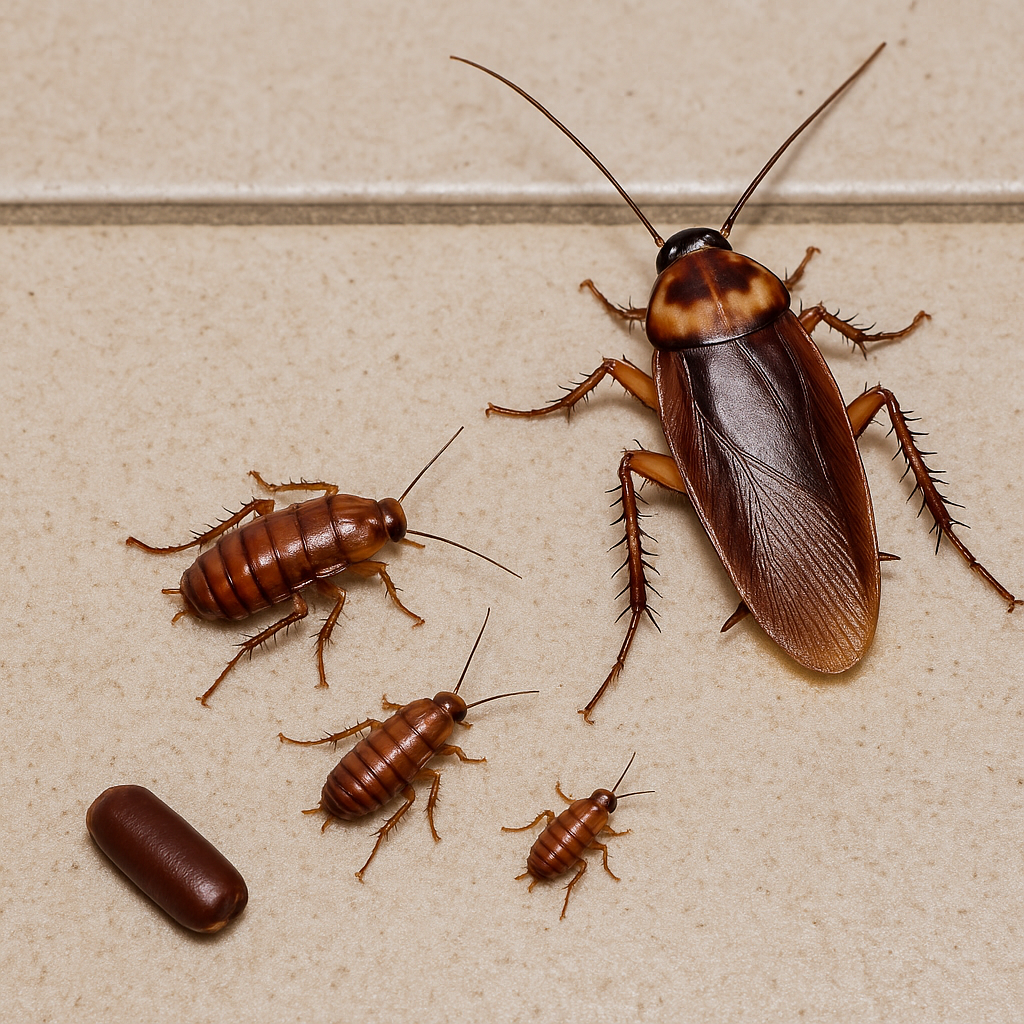
Cockroach Anatomy: Why They Thrive Everywhere
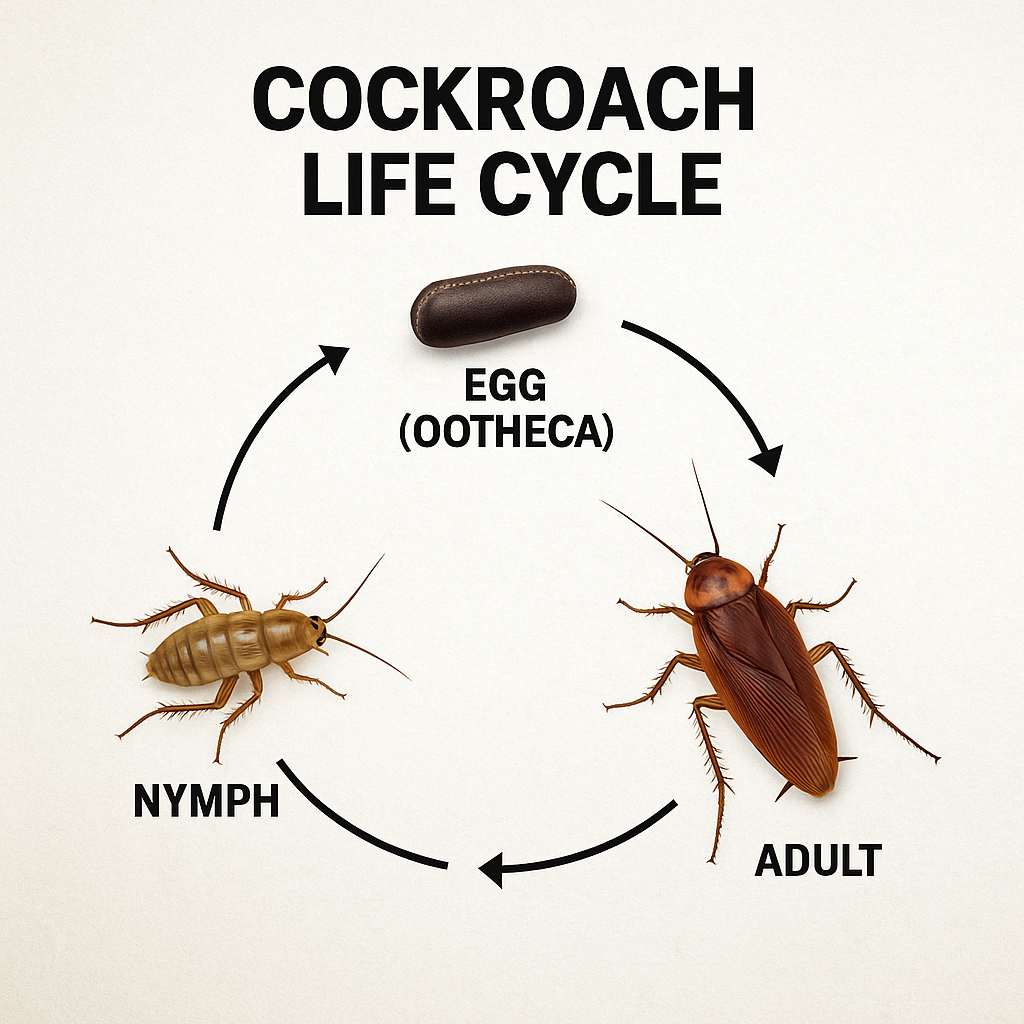
Cockroaches are built to survive. Their flat bodies allow them to squeeze through tiny cracks, while their rapid reproduction makes infestations hard to control. Some species, like the German cockroach, can produce hundreds of offspring in a year!
Why are they everywhere?
-
Resilience: Cockroaches can go weeks without food and days without water.
-
Speed: They can scurry at up to 3 miles per hour.
-
Nocturnal habits: They mostly come out at night, making them hard to spot.
-
Omnivorous diet: From leftover pizza to glue, they eat almost anything.
[Image Suggestion 2: 4K close-up of a cockroach hiding in a kitchen crevice, illustrating how they invade homes.]
Health Risks Associated with Cockroaches
1. Disease Transmission
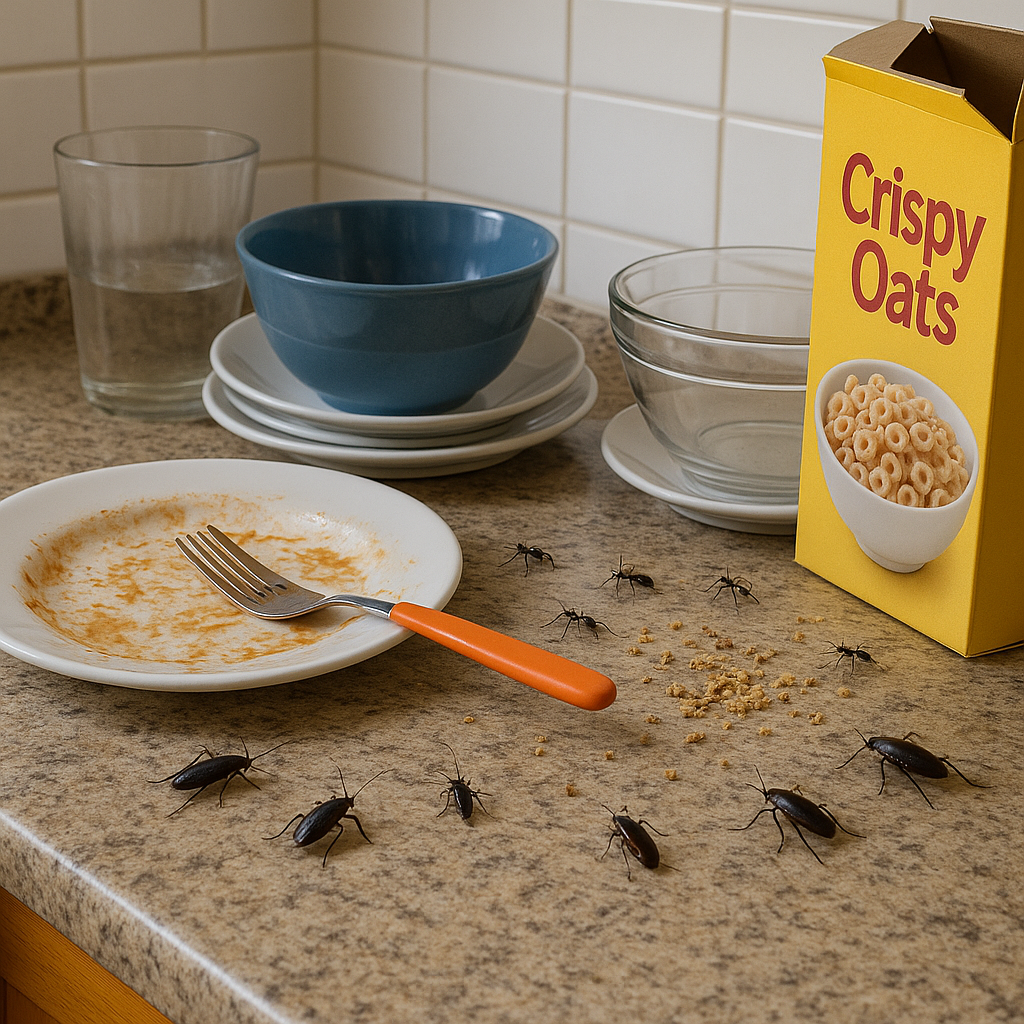
Cockroaches don’t directly cause disease, but they are major mechanical vectors for harmful bacteria and viruses. When they crawl through sewage or garbage, they pick up germs on their legs and bodies, then transfer them to countertops, food, and utensils.
Common diseases linked to cockroaches include:
-
Salmonella & E. coli: Can cause food poisoning.
-
Dysentery & Gastroenteritis: Lead to severe diarrhea and stomach cramps.
-
Cholera, Typhoid, and even Polio: Cockroaches can spread pathogens responsible for these illnesses, especially in areas with poor sanitation.
2. Allergies and Asthma
Cockroach droppings, shed skins, and saliva contain allergens that can trigger asthma attacks, especially in children. According to the World Health Organization, exposure to cockroach allergens is a significant risk factor for asthma in urban areas.
3. Contamination
Their habit of feeding on waste means cockroaches can contaminate food, surfaces, and cooking equipment, increasing your family’s risk of foodborne illness.
[Image Suggestion 3: Infographic-style 4K image showing the diseases spread by cockroaches, with icons for germs and health effects.]
Myths vs. Facts
Myth 1: Cockroaches bite people often.
Fact: While rare, cockroach bites can happen but are extremely uncommon and not their main threat.
Myth 2: All cockroaches are equally dangerous.
Fact: Some species (like German and American cockroaches) are more likely to invade homes and spread germs, while others prefer outdoors.
Myth 3: Cockroaches can survive a nuclear blast.
Fact: While more resistant to radiation than humans, cockroaches wouldn’t survive a direct nuclear explosion.
Myth 4: Only dirty homes get cockroaches.
Fact: Even spotless homes can have cockroaches—they only need warmth, moisture, and food crumbs.
[Image Suggestion 4: 4K “Myth vs. Fact” graphic with illustrations of cockroaches and common misconceptions.]
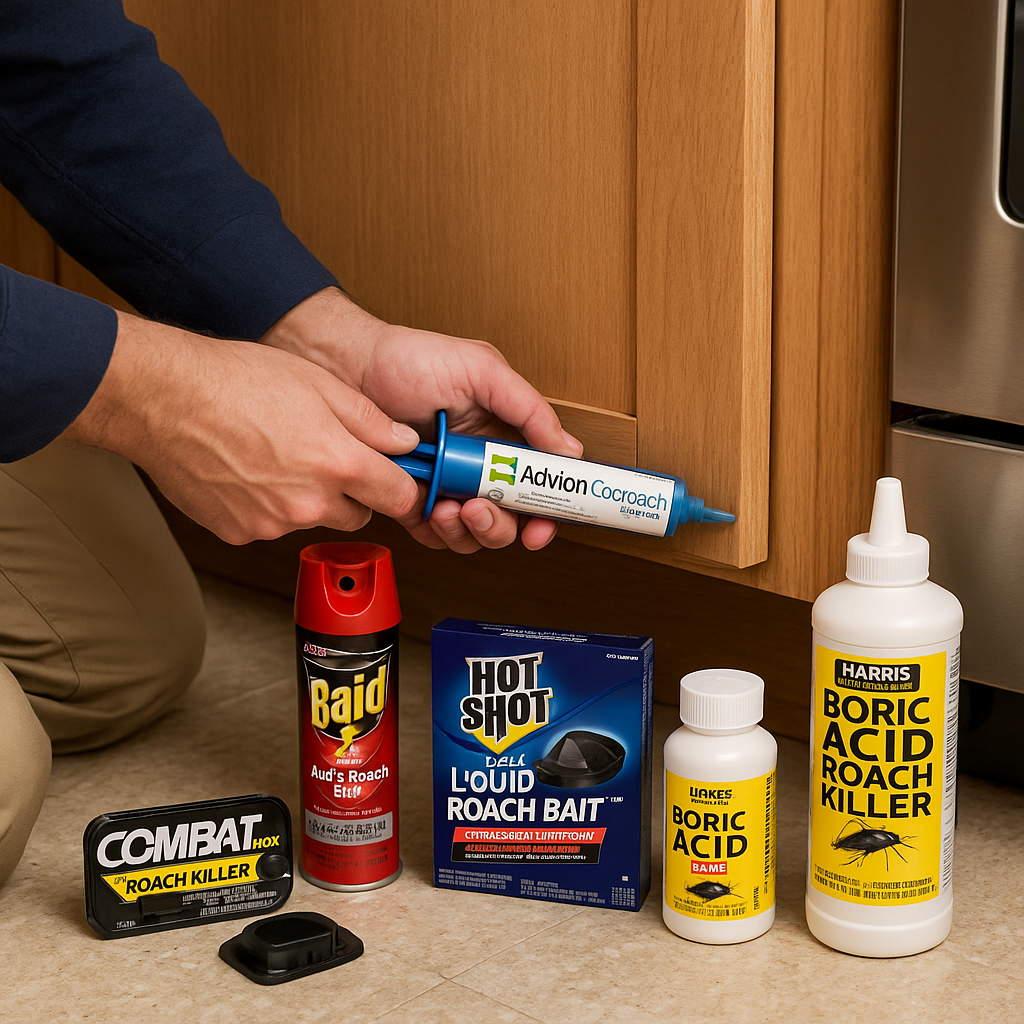
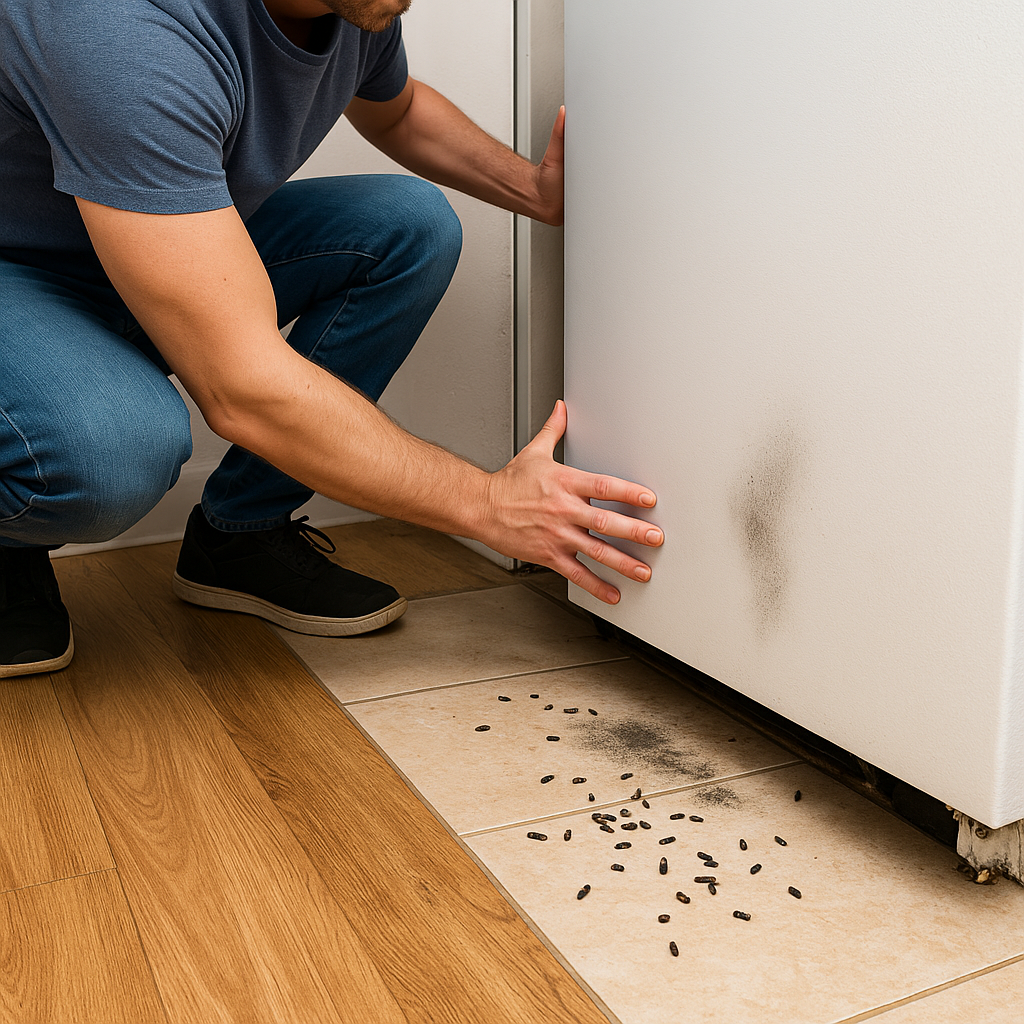
Why Cockroaches Are Hard to Eliminate
-
Rapid breeders: A single female can produce up to 400 offspring in her lifetime.
-
Hardy: Can live without their heads for a week (until they dehydrate).
-
Hiding experts: Prefer dark, hidden spaces—under sinks, behind fridges, inside wall cracks.
-
Chemical resistance: Over time, some species develop resistance to common insecticides.
Are Cockroaches Dangerous for Pets?
Cockroaches can carry parasites and bacteria that may harm your pets if ingested. Dogs and cats sometimes eat cockroaches out of curiosity, but this can lead to stomach upset or, rarely, the spread of intestinal worms.
Bottom line: Cockroaches are a health risk for everyone in the house—including pets.
[Image Suggestion 5: 4K image of a dog or cat sniffing a cockroach in a kitchen, highlighting pet risk.]
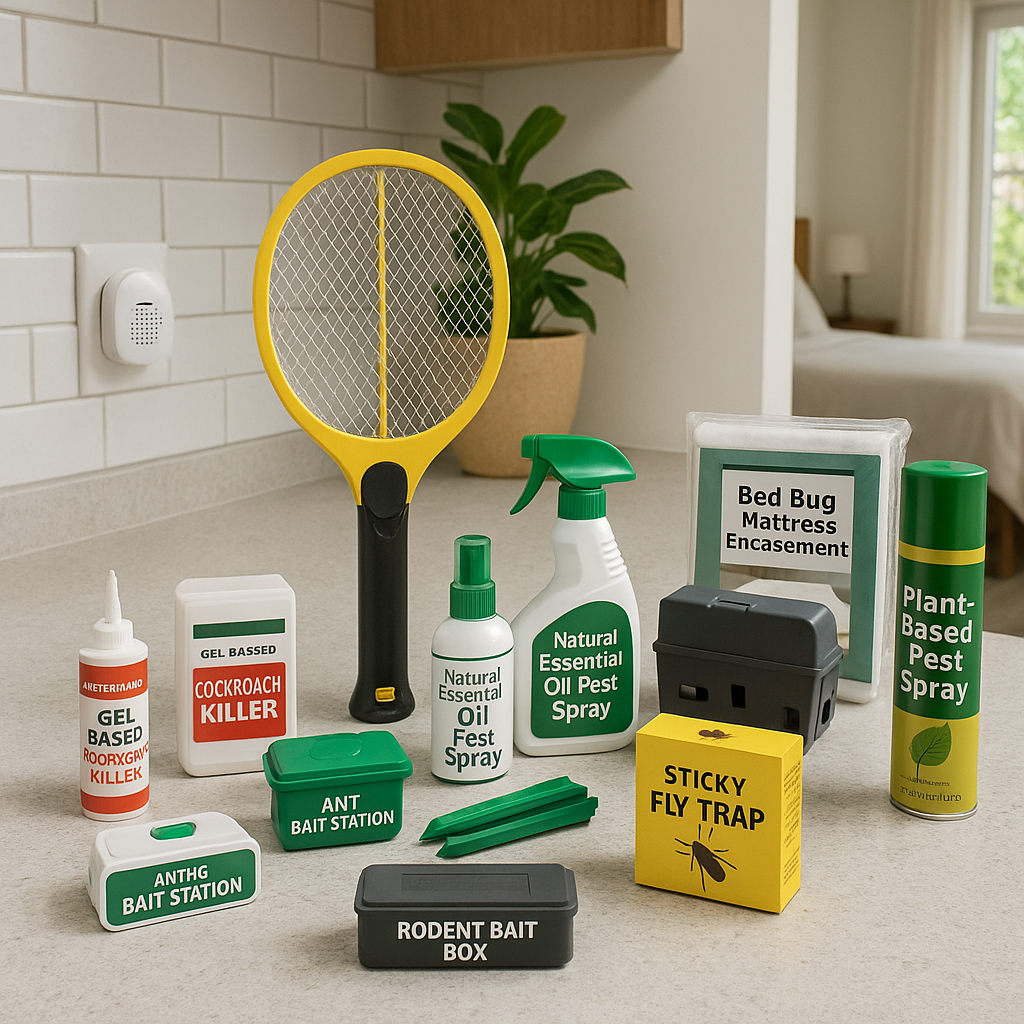
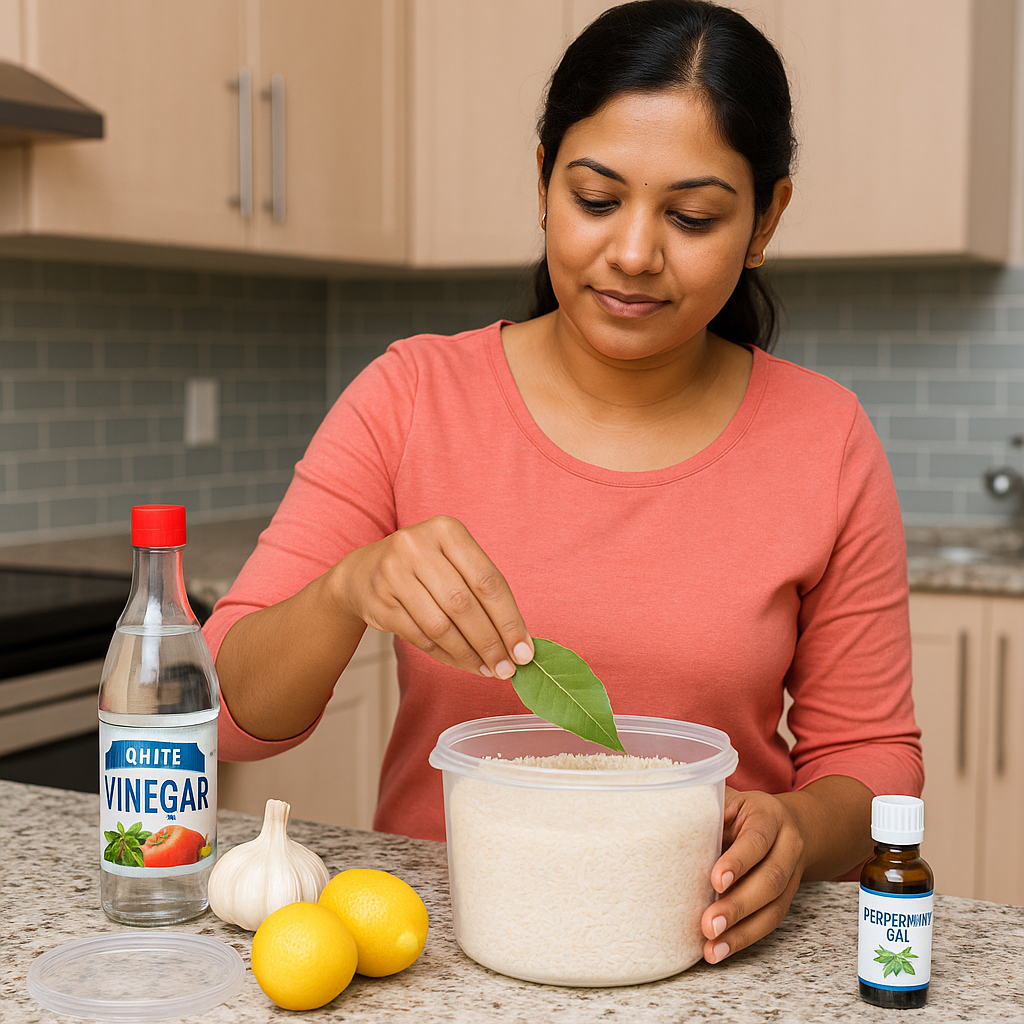
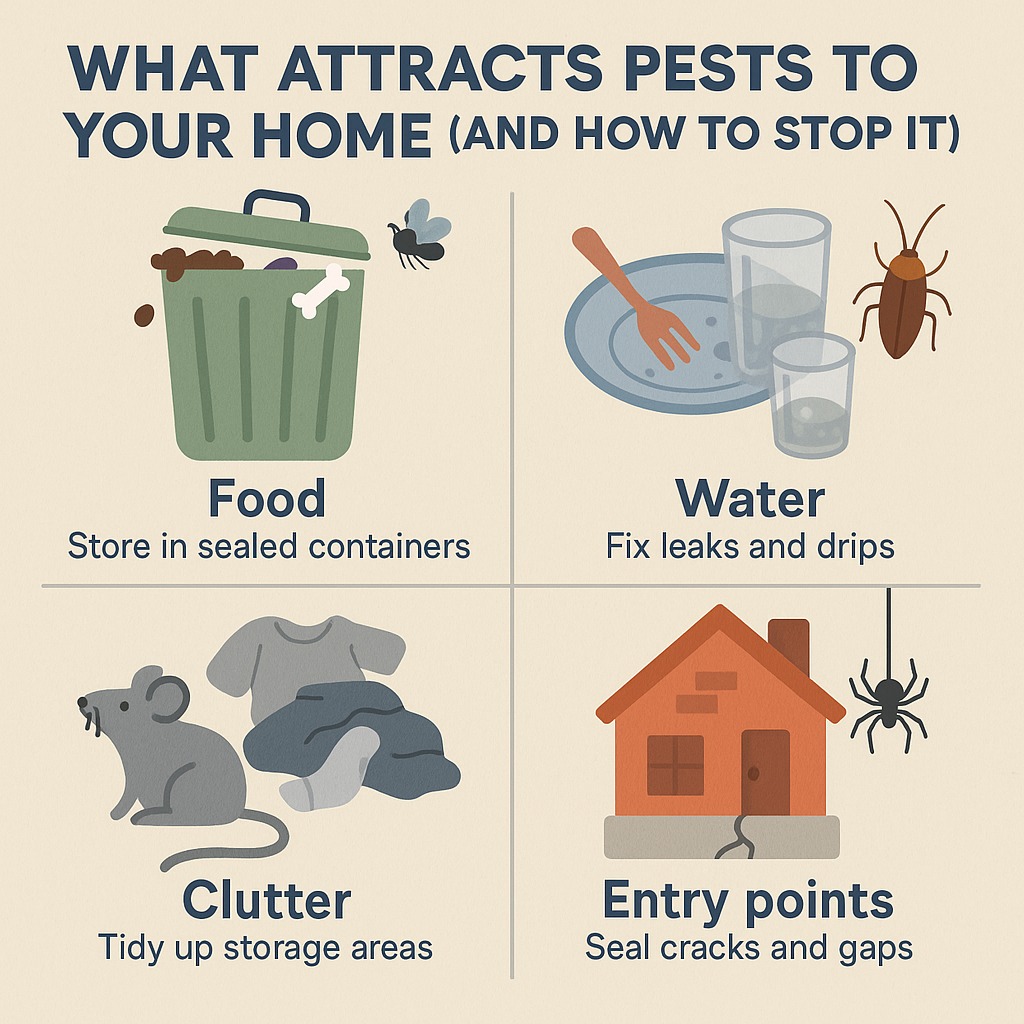
How to Protect Your Home or Business
-
Keep food sealed and stored properly.
-
Clean up crumbs, spills, and garbage regularly.
-
Fix leaks: Cockroaches love moisture.
-
Seal cracks and crevices: Block their entry points.
-
Use baits and traps for early detection.
-
Call professional pest control if infestation is severe.
Pro tip: Regular cleaning + monitoring = best defense!
Conclusion
Cockroaches are more than just a nuisance. They pose real health risks, especially in homes with children, elderly, or pets. But with good hygiene and proper pest control, you can keep your space safe.
Have you had an experience with cockroaches? Share your story or ask a question below!
Want to learn more about pest control?
Check out our other expert guides and product recommendations!




Youtube Video
Invalid YouTube URL provided.







































































































(0) Comments